New XEC Variant (KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 Recombinant): An Emerging Threat
Will the XEC Variant Be The Next Dominant COVID Strain? (Updated: 8/9/2024)
Updates:
The KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 recombinant variant is designated XEC
As of August 6th, there are 23 sequences in 7 countries
As of August 8th, there are 35 sequences in 9 countries
Estimated Growth Advantage: August 9, 2024: 97.82% (53.86% - 141.79%)
Introduction
The newly designated XEC variant is a KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 recombinant variant of SARS-CoV-2. It has been identified as a new lineage with a rapid and concerning spread across multiple countries. The early estimated growth advantage of this recombinant variant, as of August 9th is 97% (53% - 141%). In comparison, the current most prevalent variant, spreading faster than any other in the latest CDC variant proportions, has a growth advantage of 42% (40% - 42%). The margin of error is wider with XEC because it is so new but even on the low end, it beats KP.3.1.1. According to Mike Honey, it has a growth advantage of 4.6% per day. He said, on August 9th on X, “Globally, XEC is showing a robust growth advantage of 4.6% per day (32% per week) over JN.1.* + DeFLuQE variants. This is the fastest growth of any contender I am aware of. As the starting frequencies are quite low, any crossover looks like happening in September or later.”
This variant is worth identifying early because of its rapid spread, and the impact the mutations may have on the immune system. This variant combines genetic material from the KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 lineages, resulting in a unique set of mutations that may contribute to its enhanced transmissibility and potentially greater immune evasion.
U.S. Variant Proportions 7/21/2024 - 8/3/2024
Key Mutations
The recombinant variant is characterized by several notable mutations, including:
S:T22N, S:F59S ( S gene)
C18657T, C19716T (N gene)
C21627A, T21738C (ORF1ab)
T22928C, C23039G, G24872T, C25006T (S gene)
C28291A, G28884C (N gene)
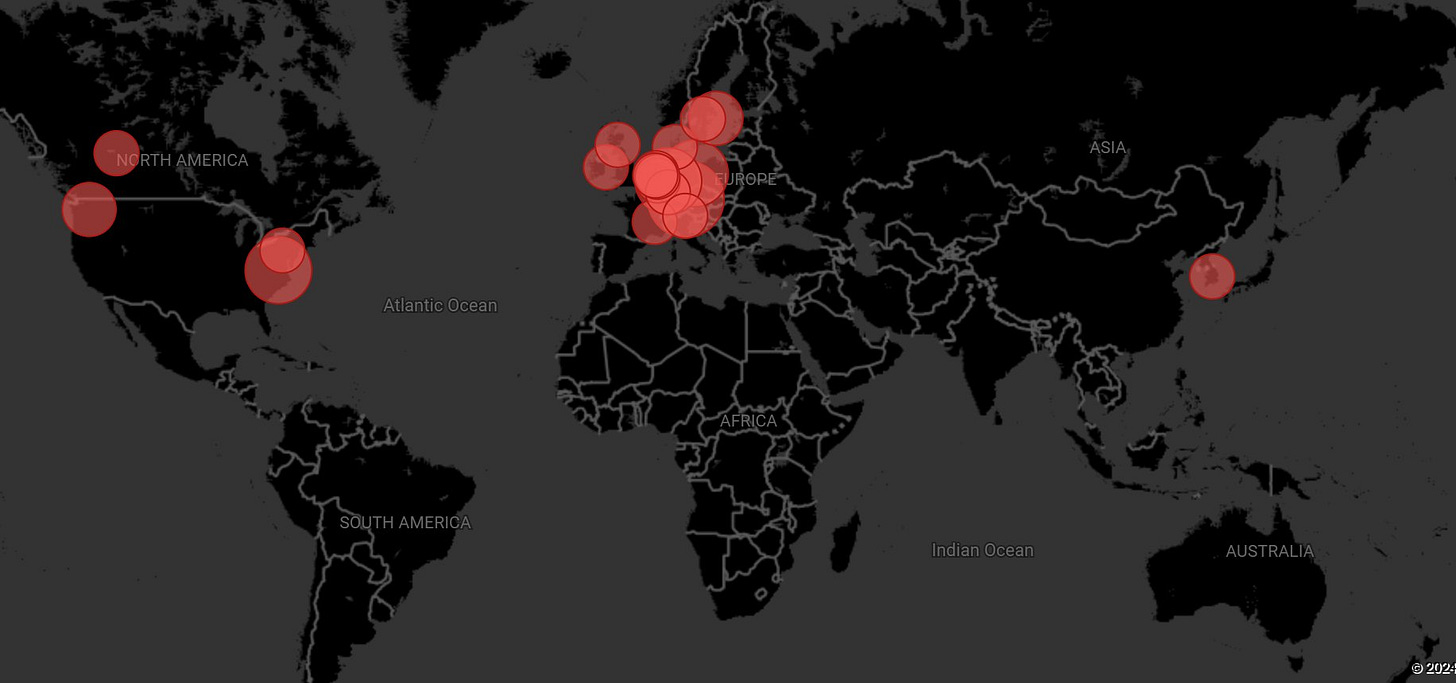
Rapid Geographic Spread
As of August 6, 2024, there were 23 sequences detected in 7 countries, showing a remarkably fast geographic spread. By August 9th, it was 36 sequences in 11 countries on 3 continents.
The list below is missing some cases.
Germany: 11 cases
Netherlands: 4 cases (from 4 separate regions)
United States: 3 cases in Virginia - 5 total
Sweden: 3 cases
France: 1 case
South Korea: 1 case
Spain: 1 case
The earliest sequence was detected on June 24, 2024, in Berlin, Germany, with the latest reported on August 8, 2024, in the U.S., Netherlands, and Sweden. The rapid spread to multiple countries within such a short timeframe is concerning.
Potential Impact
The mutations in the Spike (S) protein may enhance the virus's ability to bind to ACE2 receptors, potentially increasing infectivity. Mutations in the Nucleocapsid (N) protein could affect viral replication and immune evasion. The rapid geographic spread suggests this variant may have a transmission advantage over other circulating strains.
Conclusion
The XEC (KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 recombinant) variant's swift international spread and unique mutation profile indicate it may possess increased transmissibility and potential immune escape capabilities. Continued genomic surveillance and further studies are crucial to understand its full impact on public health. Due to how new this variant is, we have limited information on how it may impact people but we will be watching this closely and updating on further developments.
Test Accuracy
A reminder for the FDA to check the efficacy of SARS-COV-2 tests which as we reported in the last update hasn't been followed up on by the FDA since 2023.
"Our study supports the previously published observations, highlighting the importance of simultaneous use of multiple targets in SARS‐CoV‐2 diagnostic assays and continuous monitoring of genetic variability of SARS‐CoV‐2 to ensure the specificity and sensitivity of commonly used diagnostic assays. Primers and probes should be aligned with an increasing number of reported SARS‐CoV‐2 variants to reassess their suitability for SARS‐CoV‐2 diagnostics." (3)
Breakdown of Key Mutations in the KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 Recombinant Variant, XEC
N Gene Mutations
C18657T:
Location: ORF1b region
Effect: Non-structural protein (nsp14), which is involved in viral replication and transcription. (1)
C19716T:
Location: Nucleocapsid (N) gene
Effect: This mutation may impact the nucleocapsid protein, which is crucial for RNA binding and packaging of the viral genome. (1)
C28291A:
Location: Nucleocapsid (N) gene
Effect: This mutation could affect the stability and function of the N protein, potentially influencing viral replication and immune evasion.(1)
G28884C:
Location: Nucleocapsid (N) gene
Effect: Could alter the protein's interaction with host cell machinery, impacting viral assembly and release. (1)
ORF1ab Mutations
C21627A:
Location: ORF1ab region
Effect: Non-structural protein (nsp13), which has helicase activity essential for viral RNA synthesis.
T21738C:
Location: ORF1ab region
Effect: Non-structural protein (nsp13), potentially affecting its helicase function and impacting viral replication. (2)
Spike (S) Gene Mutations
T22928C:
Location: Spike (S) protein gene
Effect: This mutation occurs in the receptor-binding domain (RBD), which is critical for binding to the ACE2 receptor on host cells, potentially enhancing infectivity. (2,3)
C23039G:
Location: Spike (S) protein gene
Effect: This mutation could affect the spike protein's structure, influencing its stability and interaction with the ACE2 receptor. (2)
G24872T:
Location: Spike (S) protein gene
Effect: This mutation may alter the spike protein's ability to mediate viral entry into host cells, potentially increasing transmissibility. (2,3)
C25006T:
Location: Spike (S) protein gene
Effect: Similar to G24872T, this mutation could impact the spike protein's function and stability, affecting viral entry and immune evasion. (2,3)
S:F59S:
Location: Spike (S) protein gene
Effect: This mutation changes the amino acid at position 59 from phenylalanine (F) to serine (S), potentially altering the spike protein's structure and function.
All Mutations and Prevalence
•ORF1a:S135R (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:A211D (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:A599T (92.31%, 0.71)
•ORF1a:T842I (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:V1056L (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:G1307S (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:I1367L (7.69%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:K1973R (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:N2526S (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:A2710T (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:L3027F (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:T3090I (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:T3255I (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:P3395H (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:V3593F (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:R3821K (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:T4175I (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1a:E4388K (8.70%, 0.00)
•ORF1b:P314L (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1b:R1315C (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1b:I1566V (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF1b:T2163I (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:T19I (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:R21T (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:T22N (100.00%, 0.01)
•S:A27S (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N30I (7.69%, 0.08)
•S:S50L (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:F59S (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:V127F (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:G142D (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:F157S (96.15%, 0.00)
•S:R158G (96.15%, 0.00)
•S:L212I (96.00%, 0.00)
•S:V213G (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:L216F (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:H245N (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:A264D (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:I332V (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:G339H (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:K356T (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:S371F (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:S373P (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:S375F (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:T376A (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:R403K (95.24%, 0.00)
•S:D405N (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:R408S (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:K417N (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N440K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:V445H (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:G446S (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N450D (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:L452W (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:L455S (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:F456L (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N460K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:S477N (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:T478K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N481K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:E484K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:F486P (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:Q493E (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:Q498R (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N501Y (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:Y505H (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:E554K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:A570V (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:D614G (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:P621S (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:H655Y (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N679K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:P681R (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N764K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:D796Y (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:S939F (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:Q954H (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:N969K (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:V1104L (100.00%, 0.00)
•S:P1143L (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF3a:T223I (100.00%, 0.00)
•E:T9I (100.00%, 0.00)
•M:D3H (100.00%, 0.00)
•M:Q19E (100.00%, 0.00)
•M:T30A (100.00%, 0.00)
•M:A63T (100.00%, 0.00)
•M:A104V (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF6:D61L (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF7b:F19L (100.00%, 0.00)
•N:P13L (100.00%, 0.00)
•N:R203K (100.00%, 0.00)
•N:G204P (100.00%, 0.00)
•N:Q229K (100.00%, 0.00)
•N:S413R (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF9b:P3H (100.00%, 0.00)
•ORF9b:P10S (100.00%, 0.00)
C21T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C44T (71.43%, 0.00)
• C241T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T670G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C897A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G2060A (92.31%, 0.71)
• C2790T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C3037T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G3431T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T3565C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G4184A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C4321T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A4364C (7.69%, 0.00)
• A6183G (100.00%, 0.00)
• A7842G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C8293T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G8393A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C9344T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A9424G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C9534T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C10029T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C10198T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G10447A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C10449A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G11042T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C11563T (7.69%, 0.01)
• G11727A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C12789T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C12815T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C12880T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T13339C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G13427A (8.70%, 0.00)
• C14408T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C15714T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T15756A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C17410T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A18163G (100.00%, 0.00)
• A18492G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C18657T (100.00%, 0.03)
• C18894T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C19716T (100.00%, 0.04)
• C19955T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A20055G (100.00%, 0.00)
• T21610C (20.00%, 0.00)
• C21618T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C21622T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G21624C (100.00%, 0.00)
• C21627A (100.00%, 0.01)
• G21641T (5.00%, 0.00)
• A21651T (7.69%, 0.07)
• C21711T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T21738C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G21941T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G21987A (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22032C (96.15%, 0.00)
• C22033A (96.15%, 0.00)
• A22034G (96.15%, 0.00)
• T22200G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C22208T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C22295A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C22353A (100.00%, 0.00)
• A22556G (100.00%, 0.00)
• G22577C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G22578A (100.00%, 0.00)
• A22629C (100.00%, 0.00)
• C22674T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22679C (100.00%, 0.00)
• C22686T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A22688G (100.00%, 0.00)
• G22770A (95.45%, 0.00)
• G22775A (100.00%, 0.00)
• A22786C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G22801T (11.54%, 0.03)
• G22813T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22882G (100.00%, 0.00)
• G22895C (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22896A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G22898A (100.00%, 0.00)
• A22910G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C22916T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22917G (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22926C (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22928C (100.00%, 0.00)
• T22942A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G22992A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C22995A (100.00%, 0.00)
• T23005A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G23012A (100.00%, 0.00)
• T23018C (100.00%, 0.00)
• T23019C (100.00%, 0.00)
• C23039G (100.00%, 0.00)
• A23055G (100.00%, 0.00)
• A23063T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T23075C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G23222A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C23271T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A23403G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C23423T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C23525T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T23599G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C23604G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C23854A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G23948T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C24378T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A24424T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T24469A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G24872T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C24990T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C25000T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C25006T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C25207T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C25584T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C26060T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C26270T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G26529C (100.00%, 0.00)
• C26577G (100.00%, 0.00)
• A26610G (100.00%, 0.00)
• C26681T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G26709A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C26833T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C26858T (100.00%, 0.00)
• A27259C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G27382C (100.00%, 0.00)
• A27383T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T27384C (100.00%, 0.00)
• A27492G (11.54%, 0.09)
• C27807T (100.00%, 0.00)
• T27810C (100.00%, 0.00)
• A28271T (100.00%, 0.00)
• C28291A (100.00%, 0.00)
• C28311T (100.00%, 0.00)
• G28881A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G28882A (100.00%, 0.00)
• G28883C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G28884C (100.00%, 0.00)
• C28958A (100.00%, 0.00)
• A29510C (100.00%, 0.00)
• G29734T (22.73%, 0.00)
References:
1. Laine P, et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant with mutations in N gene affecting detection by widely used PCR primers. J Med Virol. 2022. (Link)
2. Meng B, et al. Recurrent emergence of SARS-CoV-2 spike deletion H69/V70 and its role in the Alpha variant B.1.1.7. Cell Rep. 2021. (Link)
3. Characterizations of SARS-CoV-2 mutational profile, spike protein stability, and viral transmission. PMC. 2020. (Link)




Re: A reminder to check the efficacy of SARS-COV-2 tests which as we reported in the last update hasn't been followed up on by the FDA since 2023. How do we check the current efficacy of the tests if the hey have not been updated by the FDA since 2023. Is anyone besides the FDA monitoring these tests? Do you know of any PCR or antigen efficacy results reported out in 2024?
The specimens collected in Virginia are likely from international travelers at Dulles Airport.
We need to bring back test and quarantine at the international airports if we have any hope of slowing this thing down. TACT...you haven't shown any XEC variants from Hong Kong, but I'll bet XEC can be found there...probably a LOT (but perhaps not reported).