Strategies to Avoid COVID and Other Respiratory Viruses
The most important thing that we can do is avoid getting infected in the first place. If we become infected, the goal is to limit the number of viral particles we are infected with. We want to slow viruses down at every turn so the body can mount an immune response before it spreads.
We know that many different types of viral infections can not only infect but also persist in places the immune system can’t reach. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)*, Herpes, HPV, Varicella virus (chicken pox) and HIV can all persist in our bodies outside the reach of the immune response. COVID has become extremely good at evading and suppressing the immune system during the initial, acute phase, of infection so that it can get to those hiding spots in our organs, including the brain and central nervous system. This can occur in people that have mild symptoms so everyone is at risk. Our mission is to stop that from happening.
Healthy Living: It is important to start out by pointing out the obvious. People that make an effort to take care of themselves are generally less sick. Maintain a healthy lifestyle to maximize the bodies natural immune response. Diet, sleep, and exercise are all very important in maintaining the bodies defenses to infections. With that said, even the strongest immune defenses are no match for a large dose of viral particles, that can overwhelm the system, leading to illness.
A study published December 14, 2022, found that people were less likely to get a severe COVID infection if they worked out almost any amount. People who moved around less were more likely to end up in the hospital or die from COVID, even if they only worked out for 11 minutes a week.
Ventilation: Increase ventilation as much as possible to maintain the CO2 level below 600 ppm ( ppm = parts per million) to ensure an adequate supply of fresh air is in the space and importantly, the old air building up with respiratory droplets that are potentially filled with viral particles, is being sucked out of the space.
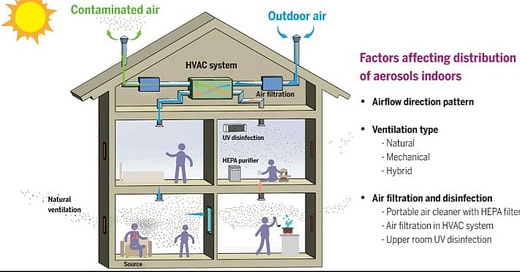
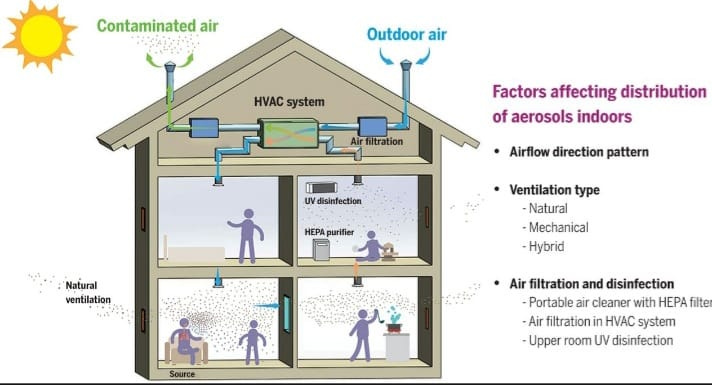
Fig. 1 Factors affecting indoor airborne transmission.
The motion of large droplets is predominantly governed by gravity. The movement of aerosols is influenced by airflow direction and pattern, and type of ventilation. Ventilation, air filtration and disinfection are important tools in preventing transmission.Monitor CO2 : Use a CO2 monitor to know when to ventilate a room. When we are outside, the CO2 levels is generally somewhere around 450 ppm. That was closer to 350 ppm not to long ago but that is another issue. Ideally we wouldn’t have the CO2 level climb over 500ppm to know that there is an adequate supply of fresh air coming into the space. However, that is hard to maintain while also retaining heat or air conditioning. The current acceptable levels are generally between 800 ppm to 1000 ppm. That is not acceptable when trying to prevent transmission of airborne pathogens, particularly one as contagious as COVID.
Build a Corsi-Rosenthal Box: This is an inexpensive, do-it-yourself air cleaner that can be easily constructed out of a box fan and MERV-13 furnace filters. The Corsi-Rosenthal Box can provide a whole-room air cleaning performance comparable to commercial HEPA air cleaners that are 10x or more the cost. Total cost is around $130USD.
Air Purifiers with a HEPA air filter: HEPA is an acronym for high efficiency particulate air. This type of air filter can theoretically remove at least 99.97% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and any airborne particles with a size of 0.3 microns (µm). COVID particles by themselves are only 0.12 microns which is smaller than what that filters, however we are not filtering individual viral particles because they are transmitted via the respiratory droplets exhaled from an infected person.
The viral particles survive inside the respiratory droplets, so by filtering the respiratory droplets, we significantly reduce the odds of exposure. If exposed then the number of particles has been significantly reduced.
Fig. 2 AI-Enabled Multiscale Computational Microscopy of Delta SARS-CoV-2 in a Respiratory Aerosol
The aerosolized respiratory droplets are usually between .2 and .5 microns. The filters alone could allow the .2 micron droplets to pass through but the smaller the droplet, the less viral particles inside of it. Check out this video of computer simulated respiratory droplets being exhaled to get an idea of how they move. The larger droplets fall however the plume of hotter exhaled air, carries the lighter smaller droplets further out and up.
When we combine measures, its called a layered strategy. Increased ventilation, air filtration significantly lower the odds of being infected and if infected, then with much fewer viral particles, giving our bodies the best possible odds.
The fewer viral particles that someone is exposed to, the easier it will be for the immune system to eliminate them because that means fewer cells will be infected and replaced, leaving us with a stronger immune system, a faster recovery, preventing a significant increase in biological age, and with any luck, avoiding longer term organ infection.
Prevent infection, first, using 1, 2, and 3 below. If exposed, then 2,3,4, and 5 can help limit the viral load in the body and help aid in recovery.
1. N-95 masks that are worn tightly to the face and around the nose are extremely effective at limiting exposure to the airborne, aerosolized respiratory droplets.
2. Gargle with mouthwash to help kill viral particles in the mouth and throat.
" A 5% (v/v) dilution of Colgate Peroxyl or povidone-iodine completely blocked viral infectivity."
"A similar 5% (v/v) dilution of Listerine or CHG had a moderate suppressive effect on the virus, but a 50% (v/v) dilution of Listerine or CHG blocked viral infectivity completely." Mouth rinses inactivated the virus without prolonged incubation."
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33804294/
3. Use a saline nasal rinse to keep viral replication and viral load lower. Helps lower odds of transmission to others. Lowers odds of COVID infecting the brain and nervous system.
"Increasing saline concentrations induce dose-dependent immediate steric hindrance in the ACE-2 receptor configuration for binding of angiotensin II, thereby inducing less virus-receptor binding"
"Nasal washes with normal saline effectively decreased the viral load during hospitalization and at follow-up."
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/crj/2022/8794127/
More detail on Saline for nasal rinse.
"The rationale for use of normal saline as inhibitor of viral replication is based on studies showing that increasing saline concentrations induce dose-dependent immediate steric hindrance in the ACE-2 receptor configuration for binding of angiotensin II, thereby inducing less virus-receptor binding [10]. Moreover, in vitro studies have demonstrated that NaCl depolarizes the plasma membrane of infected cells, leading to intracellular energy deprivation via affecting the ADP/ATP concentration ratio thus, preventing virus replication [11]. Furthermore, NaCl has been shown to inhibit 3Clpro, a viral enzyme regulating several steps of replication [12] and the host protease furin [13, 14]. Furin is used by the SARS-CoV-2 virus to prime its spikes towards fast fusion [13].
The proteolytic activity of furin was previously found to be inhibited by NaCl, starting at 75 mM (∼0.4%) onwards, and achieving >90% inhibition at 100 mM (0.6%), and complete inhibition at 200 mM (∼1.2%) [15]. In addition, saline shifts myeloperoxidase activity in nasal and pharyngeal epithelial or phagocytic cells to produce hypochlorous acid which exerts antiviral properties [16]."
* Most people don’t know that over 90% of adults have been infected with EBV.
EBV, Varicella virus (shingles), Herpes and other viruses can reactivate or really expand from the immune system’s suppression of it, when the immune system is weakened. This has been occurring after an immune suppressing COVID infection in many people, at least in part, contributing to the rates of Long COVID.
“Evidence of recent Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in individuals experiencing Long COVID”
When did most people become infected with EBV and other respiratory pathogens? The answer is, as children from transmission in between schools and homes.
“Most people are infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) during childhood or adolescence, resulting in a persistent, mostly latent EBV infection. The primary EBV infection often manifests as infectious mononucleosis (IM), especially in adolescence.”
Imagine the number of diseases that occur later in life from these viruses first acquired as children, that could be eliminated or at least significantly reduced, if we took proactive actions to prevent the transmission of these viruses and pathogens from occurring in schools. We can continue to allow this to occur or use the knowledge we have to provide a path to a healthier and longer life by preventing transmission of these pathogens in schools.
Advocating for change is never easy.
We must do better to provide a safe learning environment.
Flu, RSV, and COVID are Preventable
We have the technology, we simply must utilize it.
Click the picture below to find out more and support the campaign
to provide Clear Air for Kids.
Note: We appreciate you sharing our content with others and leaving your thoughts in the comments.