COVID Variant Update U.S. and Canada: February 18, 2023 (XBB.1.5 Impact on Vaccines)
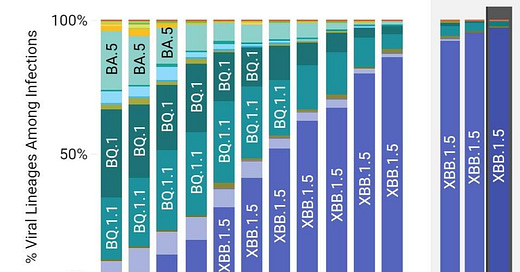
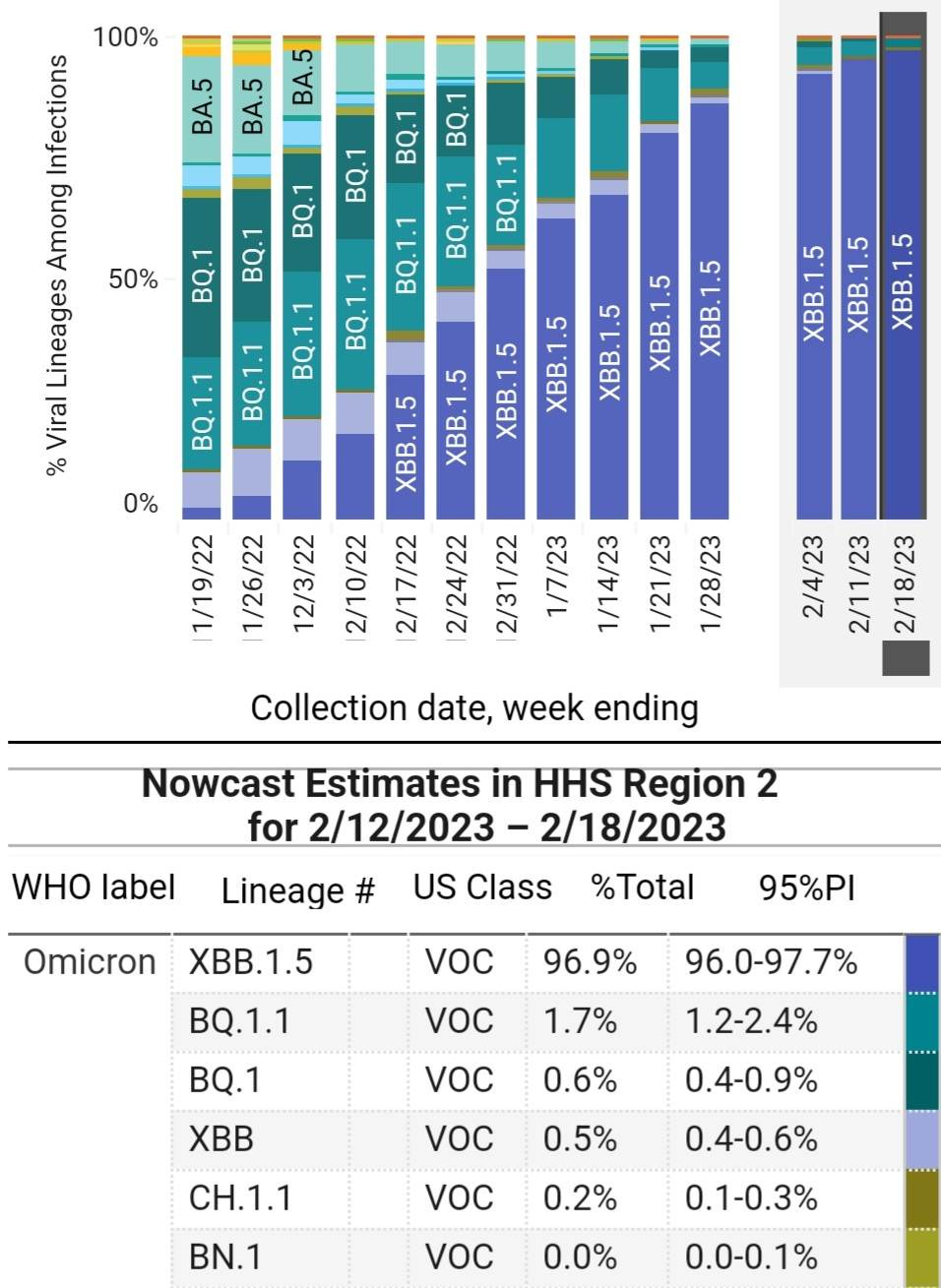
XBB.1.5 makes up over 80% of sequenced cases in the U.S.
United States
Over 96% of the cases that have been sequenced in the Northeast U.S. are caused by XBB.1.5 and its sub-variants. This variant has become the most dominant, which increases the odds that it will have its own offspring. This is exactly what is happening.
Nationally, XBB.1.5 prevalence is just over 80%. We can see that it continues to expand its reach across the U.S.
XBB.1.5 has even become dominant in the last holdout, the Northwest U.S.
Children, the elderly, and the immunocompromised remain the most vulnerable. Pediatric hospitalizations are increasing again (green line on the graph to the right)
New variants that aren’t reported in the CDC's variant proportions with a greater growth advantage over XBB.1.5.
XBB.1.5.4 : 38% growth advantage
XBB.1.5.10: 80% growth advantage
XBB.1.9.1: 120% growth advantage (Growth advantages are estimates)

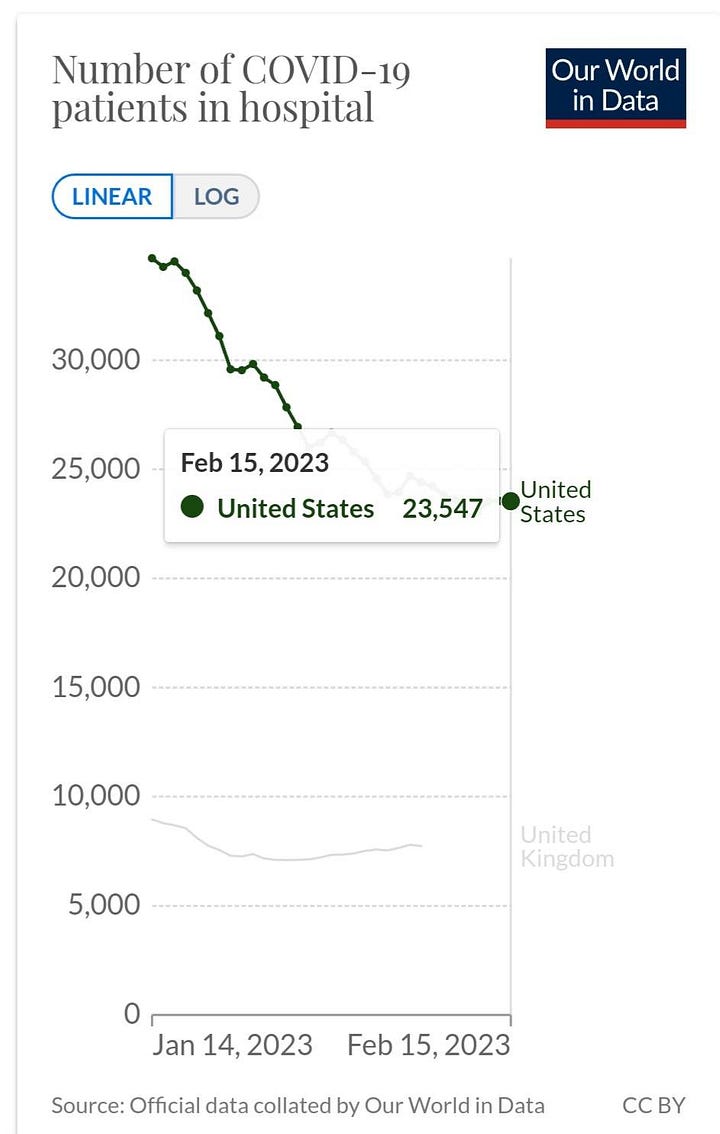
There were 23,547 COVID hospitalizations as of February 15, 2023.
There have been 429 deaths per day. (7-day average)
That means that over 3,000 people have died in the U.S. over the past 7 days. This is only what is reported.

Canada
Positivity Rates (below)
We can see that the XBB.1.5 variant is gaining momentum across Canada but at a slower pace than we have seen in the U.S. (below)
Impact on Vaccine Efficacy
Updated January 20, 2023
Authored by Toby Le
Sub-variants and Recombinants: BA.1, BA.2, BA.3, BA.4, BA.5, BA.2.12.1, BA.4/5, BF.7, BA.4.6, BA.2.75.2, BQ.1, BQ.1.1 , XBB.1, XBB1.5
January 18, 2023: Monovalent mRNA boosting (Pfizer/Moderna) produced lower neutralization titers against BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 than BA.5 by a factor of 7 and 17, respectively. Whereas for the bivalent mRNA booster, sera neutralization of BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 were lower than BA.5 by a factor 7, and 21, respectively (Miller et al. 2023).
January 17, 2023: [Pre-print] The spike protein of XBB.1.5 showed a 2.2-fold increase in infectivity in HEK293T-ACE2 cells compared to the ancestral strain spike protein. Individuals who received three dose of the Pfizer/Moderna monovalent vaccines showed reduced sera neutralization against the XBB.1.5, CH.1.1, and CA.3.1 Omicron subvariants, with 3.3-, 24.6- and 21.9-times lower neutralizing titers than the BA.4/5 variant (Qu et al. 2023).
January 12, 2023: Sera neutralization of BQ.1. and XBB were 22.2- and 25.8- fold lower than the ancestral strain in individuals who received the Moderna bivalent booster (Davis-Gardner et al. 2022).
January 9, 2023: [Pre-print] XBB and XBB.1 Omicron subvariants were highly resistant to sera neutralization by triple vaccinated (Pfizer or Moderna) individuals, with 324- and 371-fold reductions in antibody titers, respectively, compared to the ancestral strain (Jiang et al. 2023). In the same pre-print, authors found participants who received the bivalent booster as their fourth dose, had a 12-fold increase in their titer neutralization of BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 (Jiang et al. 2023).
January 5, 2023: Individuals who received three-doses of the CoroaVac vaccine prior to BA.5 breakthrough infection, had lower sera neutralization against XBB.1.5 than the ancestral strain by 40-fold (Yue et al. 2023).
January 5, 2023: In a meta-analysis by Li et al., children and adolescents who received two-doses of the Pfizer vaccine showed 50.67% and 60.59% protection against Omicron infections, respectively (Y. Li et al. 2023).
January 5, 2023: Sera neutralization was ~60% lower against the XBB.1 spike protein than the ancestral spike in vaccinated individuals (4-dose) who received the bivalent booster (Arora et al. 2023).
Source: National Collaborating Centre for Infectious Diseases, Canada
T.A.C.T. is read across 43 U.S. states and 40 countries.
T.A.C.T. has been published on Substack for 2 1/2 months and is being read in 43 U.S. states and 40 countries around the world. We would like to thank all of our Substack readers for their continued interest in the latest science and data. COVID has no concept of borders. This is impacting everyone around the world. It takes a global perspective to understand what is happening and to change the trajectory of the unsustainable path we are on.
We have an opportunity to use the cumulative science, data, and technology to provide a healthier future for our children and future generations, but we must invest the resources necessary to make this happen. This won’t happen without advocacy.
T.A.C.T. is reporting the latest science, data, and analysis in order to achieve a sustainable path forward.