COVID Kidney Infection and Associated Damage with Potential of Kidney Failure
COVID Kidney Involvement in Children
Audio Overview: The audio overview provides a general summary of the information discussed in this article. While TACT strives for accuracy, it does not guarantee the precision of every word or idea conveyed. The content is generally consistent with the science and data presented in the article below. Listen at 1, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, or 2 x speed by clicking the button on the left side of the audio.
COVID-19 has shown a significant impact on multiple organ systems, with emerging evidence highlighting its potential effects on kidney function. Studies have revealed an increased incidence of kidney involvement in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, ranging from mild symptoms to acute kidney injury (AKI). The virus has been found to target kidney cells directly, often leading to conditions such as tubulointerstitial fibrosis and other pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic responses. In severe cases, more than 30% of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 experience kidney injury, with a substantial portion requiring dialysis. Even in less severe cases, the virus's ability to invade kidney cells and disrupt immune regulation has raised concerns about long-term renal health. Understanding the scope of COVID-19's impact on kidney function is critical as it challenges patients and healthcare systems alike.
Kidney Failure Caused by COVID: COVID-related kidney failure is primarily due to direct infection of kidney cells by SARS-CoV-2, immune dysregulation, and complications like cytokine storms, blood clots, and reduced oxygen levels (hypoxia). These processes cause inflammation, fibrosis, and damage to the kidney’s filtering units, leading to acute kidney injury (AKI)
Studies have shown increased tubulointerstitial fibrosis in patients with COVID-19, suggesting potential kidney involvement. The virus can target kidney cells, causing damage by infecting them. Studies indicate more than 30% of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 develop kidney injury, and more than 50% of patients in the intensive care unit with kidney injury may require dialysis. (1)
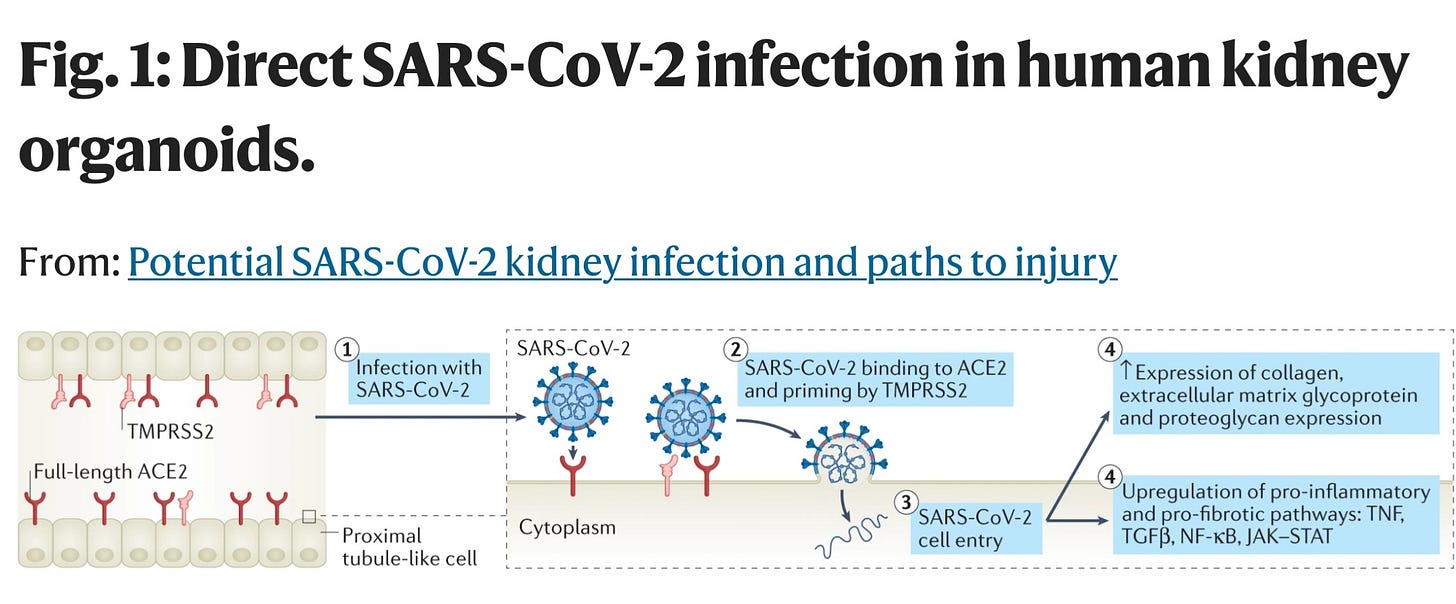
“Human kidney organoids form proximal tubule-like structures and express angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2), both of which enable the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. The virus binds to ACE2 via its spike protein, which is cleaved by TMPRSS2; this cleavage enables viral–cell membrane fusion and release of viral RNA into the cytosol. SARS-CoV-2 infection of these organoid cells results in the activation of pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory pathways. JAK, Janus kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.” https://www.nature.com/articles/s41581-022-00551-6/figures/1
Some patients with severe COVID-19 and associated kidney disease have shown positive staining for SARS-CoV-2 in kidney cells, particularly in proximal tubular cells expressing the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor.
Studies have shown that even mild cases of COVID-19 can result in kidney involvement, including direct invasion of kidney cells and immune dysregulation, potentially leading to conditions like acute tubular necrosis and IgA nephropathy.
Most common signs of kidney damage from COVID:
Reduced urine production, although sometimes urine production remains unchanged
Accumulation of fluid leading to swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
Breathlessness
Tiredness
Mental confusion
Nausea and vomiting
Lack of strength
Irregular pulse
Chest discomfort or tightness
Seizures or loss of consciousness in severe instances.
Signs of kidney problems in patients with COVID-19 include high levels of protein or blood in the urine and abnormal blood work.
Kidney involvement in children
In children, COVID-19 can also lead to kidney damage, with reports of acute kidney injury (AKI) and glomerulonephritis among pediatric patients. The impact of COVID-19 on the kidneys in children is being studied, with findings indicating various kidney pathologies associated with the viral infection.
“Even with a milder course of infection, vigilance is crucial, as various forms of kidney involvement with or without pre-existing kidney conditions may require careful monitoring among children.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10538237/
Complications related to COVID-19 affecting the kidneys include acute kidney injury, increased risk of chronic kidney disease, and potential long-term implications on kidney function even after recovery from the acute phase of the illness.
People who have COVID and co-existing, chronic conditions, including high blood pressure and diabetes are at an increased risk of kidney disease.
Kidney damage can occur in people who did not have pre-existing conditions or kidney problems before they got infected with the virus.
"SARS-CoV-2 infects the human kidney and drives fibrosis in kidney organoids" (Published: December 24, 2021)
"These results suggest that SARS-CoV-2 can infect kidney cells and might directly cause kidney injury with subsequent tubule-interstitial fibrosis."
"These data indicate that SARS-CoV-2 indeed directly infects human kidney epithelial cells including the stromal compartment."
"Results indicated increased activity of MAPK, NFκB, TNFα, and JAK-STAT in proximal tubular cells as well as MAPK and JAK-STAT pathways in podocytes (Figure 5C). Mesenchyme 1 cells showed increased MAPK, NFκB, TNFα, WNT, and TGFβ activity (Figures 5C and SB5). These pathways have all been reported to play an important role in fibroblast activation and myofibroblast differentiation and support the initiation of an injury response that might drive fibrosis."
"We here demonstrate direct infection of kidney cells in COVID-19 patients, including tubular epithelium, podocytes, and parietal epithelial cells, confirming previous findings (Bouquegneau et al., 2021; Braun et al., 2020; Müller et al., 2021; Omer et al., 2021; Puelles et al., 2020). Furthermore, our data indicate that COVID-19 patients show increased tubule-interstitial fibrosis when comparing their kidney tissue with the tissue of ICU-treated ARDS—due to influenza or other causes—patients or age-matched non-SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals, independent of pre-existing CKD prevalence. "
COVID-19 and Kidney Disease
"COVID-19 can cause acute kidney injury and may cause or exacerbate chronic kidney diseases, including glomerular diseases. SARS-CoV-2 infection of kidney cells has been reported, but it remains unclear if viral infection of kidney cells causes disease. The most important causes of kidney injury in patients with COVID-19 include impaired renal perfusion and immune dysregulation. Chronic kidney disease, especially kidney failure with kidney replacement therapy and kidney transplant, is associated with markedly increased COVID-19 mortality."
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36108262/
"Potential SARS-CoV-2 kidney infection and paths to injury" ( Published Feb 21, 2022)
"A study based largely on autopsies shows increased tubulointerstitial fibrosis in patients with COVID-19 and suggests direct kidney infection. Moreover, in human kidney organoids, SARS-CoV-2 infection upregulates several pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory pathways."
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41581-022-00551-6
"COVID-19 Symptom: Kidney Pain"
"Kidney damage is a serious and life-threatening complication that could arise from severe COVID-19"
"The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering and balancing the blood, maintaining homeostasis, and regulating many important functions in the body"
"Some signs of kidney damage from COVID include decreased urine output, swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, and breathlessness"
"Treatment for COVID kidney may include medications or even dialysis"
What causes kidney pain with COVID?
"Kidney cell targeting: The virus may infect the cells of the kidneys, as the cells have receptors that allow the virus to attach and invade, potentially causing damage to the tissue. This is similar to what has been observed in the lungs and heart. (Read more about heart palpitation and Covid-19 here)."
"Oxygen deprivation: In severe COVID-19 cases, patients may experience abnormally low levels of oxygen in the blood, which can lead to kidney malfunction. This is often due to pneumonia."
"Cytokine storms: The body's extreme immune response to the virus can lead to a cytokine storm (cytokine is a cell signaling substance), where a sudden influx of cytokines causes severe inflammation. While trying to fight the infection, this reaction can also destroy healthy tissue, including that of the kidneys."
"Blood clotting: COVID-19 can cause small clots to form in the bloodstream, which can clog the smallest blood vessels in the kidneys and impair their ability to filter toxins, excess water, and waste products from the body."
If kidney failure is suspected, you'll likely need to be hospitalized. You may undergo the following treatments depending on how COVID affects your kidneys:
Medications to balance fluid levels in the blood. If your acute kidney failure is due to a lack of fluid in your blood, your doctor may suggest receiving IV fluids. On the other hand, if you have too much fluid, leading to swollen limbs, diuretics may be prescribed to eliminate the extra fluid.
Medications to regulate potassium in the blood. If your kidneys are not effectively filtering potassium from your blood, your doctor may prescribe calcium, glucose, or sodium polystyrene sulfonate to prevent elevated potassium levels in your blood. High potassium levels can cause dangerous heart arrhythmias and muscle weakness.
Medications to restore calcium levels in the blood. If your calcium levels in the blood become too low, your doctor may recommend receiving an infusion of calcium.
Dialysis to clean toxins from the blood. If toxins build up in your blood, temporary hemodialysis, commonly referred to as simply dialysis, may be necessary to remove the toxins and excess fluid while your kidneys recover.
Dialysis can also help remove extra potassium. During the procedure, a machine removes your blood, filters out waste through an artificial kidney (dialyzer), and returns the purified blood to your body.
https://ada.com/covid/covid-19-symptom-kidney-pain/ (Published May 31, 2023)
Can kidneys recover after COVID-19?
C. John Sperati, M.D., M.H.S., an expert in kidney health says, “Patients with acute kidney injury due to COVID-19 who do not require dialysis will have better outcomes than those who need dialysis, and we have seen patients at Johns Hopkins who recover kidney function. We have even had patients in the ICU with acute kidney injury who have required dialysis, and subsequently regained their kidney function.”
“He does recommend patients with kidney issues stay away from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen. These can raise blood pressure and increase fluid volume in the body, which puts strain on the kidneys.”
As we continue to uncover the far-reaching effects of COVID-19 on various organs, the kidneys stand out as particularly vulnerable. From mild cases to severe complications requiring dialysis, the virus's ability to directly invade kidney cells poses a serious health threat. This highlights the importance of vigilant monitoring, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or those who develop symptoms of kidney involvement. While research into COVID-19’s long-term impact on kidney function is ongoing, proactive management and awareness can help mitigate risks and improve outcomes for those affected. The journey to recovery may be complex, but with continued attention and care, there is hope for a healthier future post-COVID.
Prevention is the best medicine. Avoid infections or at least mitigate the exposure to lower the risk. We must work Together Against COVID Transmission.
Another source of info.
National Kidney Foundation. Kidney disease & COVID-19
https://www.kidney.org/coronavirus/kidney-disease-covid-19#miracle-cures-and-treatments





Sarscov2 is a pernicious virus. It was designed to kill, and so it does.
In 2020-21, the people with kidney damage or who had kidney transplants, died. Almost all died.
Now, people are dying of Kidney disease and blaming other things. No one talks about covid being a stealth killer.
If you don’t die from an initial infection, wait, sarscov2 will kill you within a few years. Too many to list here.
Sirs/sepsis is killing young people. Even while in the hospital for something else, they are dying.
The good news- scientists have found an antibody that gets to the protein of sarscov2. But that doesn’t help people today. People who get infected over and over again. Cause you know, “Covid is like the flu. “