If someone you know has cancer, it's crucial to be aware of the heightened risks associated with COVID-19. Recent studies have shown that cancer patients face significantly increased risks of severe and fatal outcomes if they contract COVID-19. Additionally, there's growing evidence suggesting that the risk of being diagnosed with cancer may increase following a COVID-19 infection.
How COVID-19 Accelerates Aging and Increases Cancer Risk
COVID-19 has a unique ability to evade antibodies, making it dependent on T-cells to eliminate infected cells. Specifically, CD8-T cells are responsible for killing these infected cells. When these cells are destroyed, healthy cells must divide to replace them, a process that can lead to genetic mutations and DNA damage. This cellular division not only ages us at a genetic level but also increases the risk of mutations, particularly if we are taking certain medications during this massive cell loss and regeneration phase.
Key Points on COVID-19, Accelerated Epigenetic Aging and Cancer:
Epigenetic Age: This measures our biological age at the cellular level. Everyone ages at different speeds based on the cumulative damage to their cells and DNA.
Virus-Induced Damage: Viruses, especially those that persist, cause significant damage. Examples include EBV, HPV, Varicella, HIV, and COVID-19.
Cell Loss and Replacement: Viruses that evade antibodies can infect more cells, necessitating their elimination by CD8 T-cells, leading to further cell loss.
Increased DNA Mutations: As cells divide to replace lost ones, there’s a higher chance of DNA mutations, which can accelerate biological aging and increases the risk of cancer.
Persistent Reduction in p53 Function: p53 is crucial for regulating cell division and DNA repair. A study shows COVID causes a long-term reduction in p53 that might trigger cancer onset or exacerbate existing cancers.
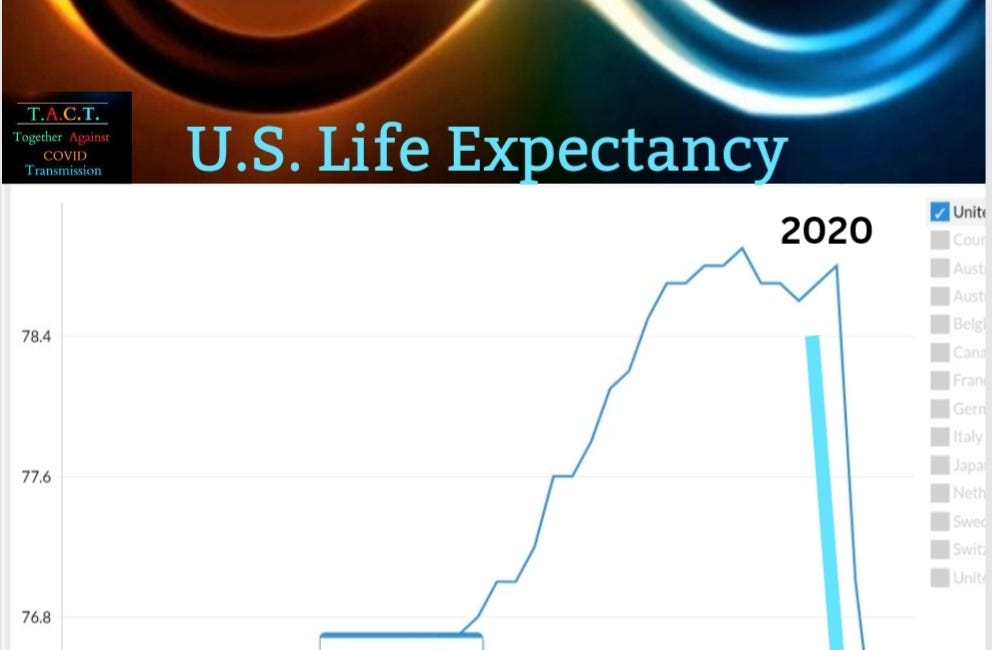
Accelerated Aging: Studies show COVID-19 can accelerate aging on various epigenetic clocks by 5 to 10 years due to the massive cell loss and division it causes.
Discover how COVID-19 increases the risk of cancer, and what this means for your health. Understand the connection between COVID, Lymphocytopenia, and cancer. Learn about the critical role of the p53 protein in preventing tumor development and how a persistent reduction in its function could trigger oncogenesis. We also provide vital recommendations for protecting individuals, such as the importance of N-95 masks, air purifiers, and improved ventilation. Subscribe now to stay informed about the latest research and practical tips to safeguard your health and the health of your loved ones.
COVID-19's Impact on Cancer Patients
A study titled "Systemic Anticancer Therapy and Thromboembolic Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients With Cancer and COVID-19" highlighted that cancer patients undergoing systemic anticancer therapies within three months before contracting COVID-19 faced a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE). These patients experienced worse outcomes compared to those not receiving such therapies. This underscores the need for close monitoring and potential thromboprophylaxis for cancer patients with COVID-19.
Study Highlights:
Risk of VTE: Higher in patients receiving endocrine therapy, VEGFis/TKIs, IMiDs, ICIs, and chemotherapy compared to those not receiving systemic therapies.
Outcomes: Patients with VTE had higher rates of ICU admission and mechanical ventilation, with a greater relative risk of death.
Is SARS-CoV-2 an Oncogenic Virus?
"Oncogenic" refers to anything that has the potential to cause or promote the formation of cancer. Specifically, it describes substances, viruses, genes, or other agents that can induce the transformation of normal cells into cancerous cells. For example, certain viruses like human papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) are considered oncogenic because they can lead to cancer development in infected individuals. Similarly, certain genes, when mutated, can become oncogenic and contribute to the uncontrolled growth and division of cells, leading to tumor formation.
COVID Causes Lymphocytopenia (1)
"Lymphocytopenia is also a risk factor for the development of cancers and autoimmune disorders."
Understanding the Connection Between COVID, Lymphocytopenia, and Cancer Risk
Lymphocytopenia, a condition characterized by an abnormally low level of lymphocytes in the blood, can significantly increase the risk of developing cancer. Lymphocytes, which include T-cells, B-cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, are crucial components of the immune system responsible for fighting off infections and monitoring the body for abnormal cell growth, such as cancer cells.
How Lymphocytopenia Increases Cancer Risk
Impaired Immune Surveillance:
Lymphocytes play a critical role in identifying and destroying cancerous or pre-cancerous cells. When their numbers are depleted, the body's ability to detect and eliminate these abnormal cells is compromised, increasing the risk of cancer development.
Increased Susceptibility to Infections:
Patients with lymphocytopenia are more prone to recurrent infections and infections with unusual organisms, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, cytomegalovirus, rubeola, and varicella pneumonias, which can often be fatal. Persistent infections and chronic inflammation can create an environment conducive to cancer development by causing continuous cellular damage and stimulating abnormal cell growth.
Reduced Effectiveness of Tumor Suppression:
Certain lymphocytes, like cytotoxic T-cells and NK cells, are directly involved in killing cancer cells. A reduction in these cells diminishes the body's natural tumor-suppressing mechanisms, allowing cancer cells to proliferate unchecked.
Impact of COVID-19:
COVID-19, along with AIDS, is one of the leading causes of lymphocytopenia. The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19, can cause a significant drop in lymphocyte counts, weakening the immune system. This increased vulnerability to infections and impaired immune function can lead to higher cancer risk. (1)
“Because p53 is essential for regulating DNA repair and cell division, it has been nicknamed the "guardian of the genome." (4)
COVID Causes Persistent Reduction of p53 Protein
Another study explored whether SARS-CoV-2 could be oncogenic. It showed that the p53 protein, which acts as a tumor suppressor, might be persistently reduced following severe COVID-19 infection. A reduction in p53 function could increase the risk of cancer, as p53 is crucial for regulating cell division and DNA repair. This long-term reduction in p53 might trigger cancer onset or exacerbate existing cancers.
Key Findings:
TP53 Gene: Provides instructions for making the tumor protein p53, which regulates cell division and prevents tumor development by repairing damaged DNA or inducing apoptosis in damaged cells.
COVID-19 Impact: Persistent reduction of p53 after COVID-19 could lead to an increased risk of oncogenesis, similar to pathogenic mutations in TP53.
Protecting Patients
Given these risks, it's vital to demand that healthcare professionals take appropriate precautions:
N-95 Masks: Essential for caregivers of cancer patients, the immunocompromised, and other high-risk groups.
Air Purifiers: Patient rooms should be equipped with air purifiers with HEPA filters to ensure clean air and better outcomes.
Ventilation: To protect patients, rooms should maintain CO2 levels at or below 600 ppm, use HEPA or MERV 13 filters, and ensure proper ventilation to reduce viral particles.
Conclusion
COVID-19 not only poses a direct threat through infection but also indirectly by accelerating epigenetic aging and increasing the risk of cancer through mechanisms such as the significant reduction of lymphocytes and the persistent reduction of the p53 protein. Protecting patients with rigorous precautions is essential to mitigate these risks.
We must demand that healthcare professionals wear N-95 masks when caring for any patient but even more so for cancer, immunocompromised, dementia, diabetes, and other high-risk patients. All patient rooms should have air purifiers with HEPA filters until hospitals upgrade their HVAC systems. Clean air increases the odds of better outcomes.
Read more about COVID Accelerated Aging.
COVID Accelerated Aging
COVID Accelerated Aging Epigenetic Age is a measure of our age at the cellular & DNA level. Everyone ages at different speeds based on the damage to our cells and DNA over time. Damage occurs from viruses and can be more damaging if the virus persists.
Sources with Highlights:
1. MSD Manual - Professional Version: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/hematology-and-oncology/leukopenias/lymphocytopenia
2. "Systemic Anticancer Therapy and Thromboembolic Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients With Cancer and COVID-19" (published Aug 17, 2023)
Key Points
Question Is there an association between systemic anticancer therapy and the risk of thromboembolic events in hospitalized patients with cancer and COVID-19?
Findings In this cohort study of 4988 hospitalized patients with cancer, patients with active cancer and COVID-19 had a higher risk of developing venous thromboembolism when exposed to systemic anticancer therapies within 3 months prior to COVID-19 diagnosis compared with patients not receiving systemic therapy. Patients with COVID-19–related thromboembolic events who were receiving systemic therapies experienced worse outcomes compared with those not receiving such therapies.
Meaning Patients with cancer and COVID-19 need close monitoring for thromboembolism and consideration for risk-mitigating thromboprophylaxis, especially if recently exposed to systemic anticancer drugs.
Conclusions and Relevance In this cohort study, the relative risk of developing VTE was high among patients receiving TOIs and varied by the type of therapy, underlying risk factors, and demographics, such as race and ethnicity. These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and perhaps personalized thromboprophylaxis to prevent morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19–related thromboembolism in patients with cancer.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2808502
3. "Is SARS-CoV-2 an oncogenic virus?"
"We show convergent evidence from three different transcriptomic datasets and techniques that represent a molecular proof of concept that p53 may be acutely and persistently reduced after severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. A persistent reduction of the p53 tumor suppression functions, as might be the case in long-COVID-19 severe patients, may constitute a risk factor for oncogenesis comparable to pathogenic mutations in TP53. Such long-term reduction of p53 might trigger cancer onset or contribute to worsen the course of patients with an ongoing tumoral process."
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9361571/
4. Article: TP53 gene - Tumor protein p53
"The TP53 gene provides instructions "The TP53 gene provides instructions for making a protein called tumor protein p53 (or p53). This protein acts as a tumor suppressor, which means that it regulates cell division by keeping cells from growing and dividing (proliferating) too fast or in an uncontrolled way."
"The p53 protein is located in the nucleus of cells throughout the body, where it attaches (binds) directly to DNA. When the DNA in a cell becomes damaged by agents such as toxic chemicals, radiation, or ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight, this protein plays a critical role in determining whether the DNA will be repaired or the damaged cell will self-destruct (undergo apoptosis). If the DNA can be repaired, p53 activates other genes to fix the damage. If the DNA cannot be repaired, this protein prevents the cell from dividing and signals it to undergo apoptosis. By stopping cells with mutated or damaged DNA from dividing, p53 helps prevent the development of tumors."
Because p53 is essential for regulating DNA repair and cell division, it has been nicknamed the "guardian of the genome."
Clean Air For Kids
For these reasons and many more not mentioned here, we have to protect children while sitting in classrooms. Increasing ventilation to levels that keep the CO2 level at 600ppm or less. This ensures that the ventilation is pulling in enough fresh air and it helps kill viral particles remaining in the air at a much faster pace. It takes approximately 40 minutes for viable virus particles to become inactivated with CO2 below 620 ppm, instead of an hour or longer when CO2 is higher.
Higher oxygen content is good for the brain and it helps ensure COVID viral particles aren't building up in the room. We also need to add HEPA or at least Merv 13 filters to filter out pathogens from the air. This protects children's health and education while also protecting their parents/caregivers and teachers from viruses, bacteria, allergens, and other pathogens that are otherwise floating around classrooms.
#Cancer #COVIDCancer #thromboembolism #CAA #COVIDAcceleratedAging




Hi TACT...Thanks for keeping at this. It must be rather discouraging, however, since seemingly everyday a new threat emerges on the horizon.
On the topic of Covid & Cancer, here is an interesting paper (if you haven't seen it).
I will highlight the 'money paragraph'...
"Because IgG4 has no direct influence on cancer cell proliferation, these findings unambiguously indicate that cancer cells utilize the IgG4 antibody to block local immunological responses and thus allow cancer growth in vivo via immune escape."
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10222767/